Backfeeding a generator is not recommended and can be very dangerous. Backfeeding refers to connecting a portable generator directly to your home’s electrical panel without a transfer switch. This can lead to a phenomenon called “islanding,” where the generator continues to power your home’s electrical circuits even when the main power is restored. This poses a significant risk to utility workers trying to restore power and can also damage your generator or electrical equipment.
To ensure safe and proper use of a generator, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and install a transfer switch. A transfer switch allows you to safely switch between the generator power and the utility power, preventing any potential hazards. If you are not familiar with electrical systems or have doubts, it is best to consult a licensed electrician for assistance.
Let’s explore the reasons why backfeeding is unsafe and the importance of using proper equipment to protect yourself and others.

What Is Backfeeding a Generator?
Backfeeding is when electricity flows from your generator into your electrical system in the opposite direction. This can be extremely dangerous and is also illegal. When backfeeding occurs, the electricity from your generator can flow back into the utility lines, creating a hazardous situation for utility workers and others. It can cause injury or even death.
Not only that, but backfeeding can also cause damage to your equipment and appliances. It can overload circuits and cause components to fail. To prevent backfeeding and ensure the safety of everyone involved, it is important to use a transfer switch.
A transfer switch is an electrical switch that connects your generator to your electrical system. It safely and quickly switches the electrical load from the utility power source to the backup power source during a power outage. By using a transfer switch, you can avoid the risks associated with backfeeding and ensure that only one power source is connected to your electrical system at a time.
Potential Risks of Backfeeding a Generator
Backfeeding allows electricity to flow in both directions, including back into utility lines, which can be extremely dangerous for utility workers and anyone nearby.
Additionally, backfeeding can cause damage to your equipment and appliances, overload circuits, and lead to component failures.
To ensure your safety and the proper functioning of your electrical system, it is crucial to install a transfer switch. This switch will isolate your backup power source, like a generator, when it is not in use and connect it to your electrical load only when necessary.
Basic Safety Measures for Backfeeding a Generator
1. Protective Gear and Equipment Needed to Backfeed a Generator
Proper protective gear and equipment are essential for safely connecting a generator to a household electrical system. When backfeeding a generator, it is crucial to prioritize your safety and the safety of others.
- Start by wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety glasses, gloves, and non-conductive footwear. These will protect you from potential electrical hazards and ensure a secure connection.
- Additionally, use insulated tools specifically designed for electrical work to minimize the risk of electrical shock.
- Before connecting the generator, make sure it is properly grounded to prevent electrical surges and short circuits.
- Use heavy-duty extension cords with adequate amp ratings to handle the load and avoid overheating.
- Finally, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and consult with a licensed electrician for guidance on proper equipment and gear to ensure a safe and efficient backfeeding process.
2. Requirements Of the National Electrical Code (NEC) For Backfeeding Generators
To comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements for backfeeding generators, you must ensure that your electrical system is properly equipped with a transfer switch or interlock kit. The NEC mandates these safety measures to prevent dangerous situations, protect utility workers, and avoid damage to equipment and appliances.
- A transfer switch is an electrical switch that connects a backup power source, like a generator, to your building’s electrical system. It safely and quickly switches the electrical load from the utility power source to the backup power source during a power outage. Transfer switches isolate the backup power source when not in use and connect it to the electrical load when needed.
- Another option is an interlock kit, which connects a generator to an electrical panel safely. It consists of a metal plate and a mechanical interlock, preventing simultaneous power from the utility and generator.
These measures ensure the safety and reliability of your electrical system, providing peace of mind during power outages.
3. Grounding Requirements When Backfeeding a Generator
Grounding is crucial when connecting a generator directly to an electrical system without a transfer switch. Without proper grounding, there is a risk of electrical shock and damage to equipment.
To ensure safe operation, follow these grounding requirements:
- Install a grounding electrode system: This involves driving a copper or galvanized steel rod into the earth near the generator. The rod should be at least 8 feet long and driven deep enough to ensure good contact with the soil.
- Connect the generator to the grounding electrode: Use a copper grounding wire with a minimum gauge of 6 AWG to connect the generator’s grounding terminal to the grounding electrode. Ensure a tight and secure connection.
- Bond the generator to the electrical system: Use a copper bonding wire with a minimum gauge of 6 AWG to connect the generator’s grounding terminal to the grounding bus bar in the electrical panel. This ensures that the generator and the electrical system have the same reference point for grounding.
- Test the grounding: Use a ground impedance tester to measure the resistance between the generator’s grounding electrode and the earth. The resistance should be below the recommended limit to ensure effective grounding.
By following these grounding requirements, you can minimize the risk of electrical hazards and ensure the safe operation of your generator when connecting it directly to an electrical system without a transfer switch.
Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a qualified electrician if you have any doubts or questions.
4. Electrical Load Considerations When Backfeeding a Generator
When backfeeding a generator into an electrical system, it’s important to consider the electrical load to prevent overloading circuits and causing damage.
To ensure safe and efficient operation, you need to understand the power requirements of your electrical devices and appliances. Start by calculating the power demand of each circuit or individual device that will be connected to the generator. This can be done by multiplying the voltage (usually 120 or 240 volts) by the current in amps.
Sum up the power demands of all the circuits to determine the total electrical load. It’s crucial to ensure that the generator’s capacity exceeds the total load to avoid overloading. Remember, overloading can lead to overheating, equipment failure, and potential safety hazards.
Power Inlet Boxes and Transfer Switches: What Are They and Do I Need Them?
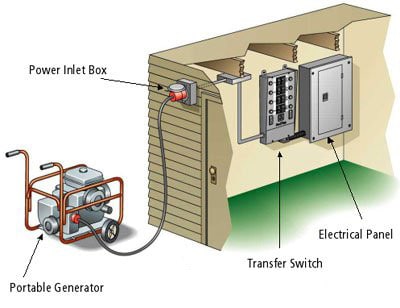
When connecting a generator to your home’s electrical system, it is important to consider the use of power inlet boxes and transfer switches.
1. Power Inlet Boxes for Connecting Generators to Your Home’s Electrical System
An alternative to using transfer switches for connecting generators to your home’s electrical system is using power inlet boxes. Power inlet boxes provide a safe and convenient way to connect your generator directly to your electrical panel.
These boxes are installed on the exterior of your home, allowing you to easily plug in your generator’s power cord. Power inlet boxes are designed to meet electrical code requirements and provide a secure connection. They feature a weatherproof enclosure to protect the connections from the elements. Inside the box, there are terminals where you can connect your generator’s power cord.
To connect your generator using a power inlet box, you will need to install a dedicated circuit breaker in your electrical panel. This breaker will be connected to the power inlet box and provide power to the circuits you want to energize during a power outage.
Using a power inlet box eliminates the need for manual transfer switches and allows for a seamless switch between utility power and generator power. It ensures that only one power source is connected to your electrical system at a time, preventing backfeeding and potential damage to your equipment.
When installing a power inlet box, it is important to follow local electrical codes and guidelines. It is recommended to consult a licensed electrician to ensure proper installation and adherence to safety standards.
2. Transfer Switches: Manual vs. Automatic
The difference between manual and automatic transfer switches lies in their ability to detect power failures and switch power sources.
A manual transfer switch requires manual operation to switch between the utility power source and the backup power source, such as a generator. It is typically operated through a lever or switch, allowing you to manually control the power source during a power outage.
On the other hand, an automatic transfer switch is equipped with sensors that can detect power failures and automatically switch to the backup power source. This eliminates the need for manual operation and ensures a seamless transition between power sources.
With an automatic transfer switch, you can have peace of mind knowing that your backup power will kick in automatically when needed, providing a reliable and uninterrupted power supply.
In Short, What Is a Circuit Breaker? And What to Consider When Selecting the Right Circuit Breaker for Your Application
A circuit breaker is an electrical device that automatically interrupts or breaks the flow of electric current in a circuit when it detects a fault or overload. It protects electrical circuits and devices from damage caused by excessive current by preventing overheating or fire hazards.
Selecting the right circuit breaker for your application can ensure the safe and efficient distribution of electrical power.
When choosing a circuit breaker, it is important to consider factors such as the voltage rating, current rating, and interrupting capacity.
The voltage rating should match the voltage of your electrical system to ensure proper operation. The current rating should be selected based on the maximum current that will flow through the circuit breaker. It is crucial to choose a circuit breaker with an interrupting capacity that can handle the maximum fault current that may occur.
Additionally, consider the type of circuit breaker that is suitable for your application, such as thermal-magnetic or electronic trip units.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Backfeed My Generator Without Any Safety Measures?
No, you should never backfeed your generator without safety measures. It’s dangerous and illegal. Backfeeding can harm utility workers and others, damage equipment, and create hazardous conditions. Use a transfer switch or interlock kit for proper and safe generator connection.
What Are the Consequences of Backfeeding a Generator Without a Transfer Switch?
Backfeeding a generator without a transfer switch can have serious consequences. It is dangerous and illegal, posing risks of injury or death to utility workers and others. It can also cause damage to equipment and appliances.
How Can I Ensure the Safety of Utility Workers When Using a Generator?
To ensure the safety of utility workers when using a generator, it is essential to avoid backfeeding by connecting a transfer switch. This prevents electricity flowing into utility lines, protecting workers from injury or death.
What Is the Purpose of a Power Inlet Box in Generator Backfeeding?
The purpose of a power inlet box in generator backfeeding is to provide a safe and convenient connection point for the generator’s power cord. It allows you to easily connect and disconnect the generator without the need for direct wiring to the electrical system.
How Do Circuit Breakers and Breaker Panels Play a Role in Backfeeding a Generator?
Circuit breakers and breaker panels play a crucial role in backfeeding a generator. They help protect your electrical system from overload and damage by interrupting the flow of electricity when a fault occurs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is crucial to prioritize safety when it comes to generator backfeeding. The risks associated with backfeeding, such as endangering utility workers and causing equipment damage, cannot be overlooked.
To ensure a safe connection between your generator and electrical system, the use of transfer switches is highly recommended. These switches act as a safeguard, isolating the backup power source when not in use and seamlessly switching the electrical load during power outages.
Remember, ‘an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure’ – investing in the right equipment now can save lives and prevent costly damages in the future.






