In today’s technologically advanced world, it is estimated that approximately 80% of households in developed countries rely on inverters to power their appliances. With the increasing demand for uninterrupted electricity supply, choosing the right inverter becomes crucial in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of our appliances.
An inverter acts as a bridge between a 12V battery system and 240V appliances, converting DC power to AC power. However, selecting the appropriate size is paramount to prevent potential hazards such as battery damage or fire risks. Power consumption of the appliances, along with a margin for peak power draw, must be carefully considered.
Additionally, the maximum discharge specifications of the battery system, as well as suitable cabling and fuses, should be taken into account. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on choosing the right inverter, emphasizing safety measures and the importance of matching inverter size with appliance and battery system requirements.
What is an inverter?
An inverter is a device that converts 12V power from a battery system into 240V power, allowing for the operation of appliances in a safe and efficient manner. It serves as a crucial component in running 240V appliances from a 12V battery system.
By converting the lower voltage power to the higher voltage required by the appliances, the inverter enables them to function as intended. This conversion process must be carefully executed to avoid damaging the batteries or creating fire hazards.
It is important to choose the right size inverter for the specific power consumption of the appliances, including a margin for peak power draw. Additionally, considerations such as battery discharge specifications, cabling, and fuses must be taken into account to ensure a safe and optimal setup.
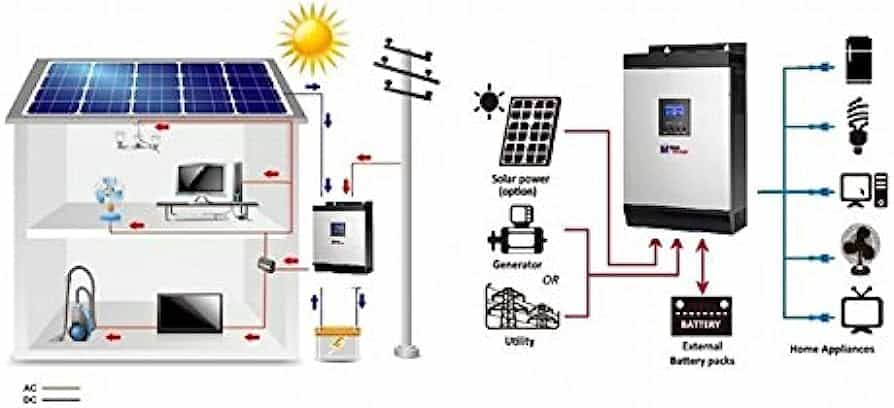
Power Consumption Considerations
When determining the appropriate size of an inverter, careful consideration of the power consumption of the appliances is necessary, taking into account both their rated power and potential peak power draw.
To ensure a safe and efficient power supply, the following factors should be considered:
- Appliance power ratings: Check the stickers or labels on the appliances to find their power consumption. For example, a toaster may consume 700-1200W, while a kettle may require 1600-2200W.
- Peak power draw: Appliances may have a higher power demand during startup or specific operations. It is important to add a margin for peak power draw to avoid overloading the inverter.
- Inverter capacity: It is recommended to choose an inverter with at least 30% extra capacity above the highest-rated appliance. This ensures that the inverter can handle sudden power surges without issues.
- Battery system limitations: Consider the maximum discharge specifications of the battery system to ensure it can handle the power demands of the chosen inverter and appliances.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the right size inverter to safely power your appliances while avoiding potential damage to your battery system.
Matching Inverter Size
By carefully considering the power consumption of your appliances and the limitations of your battery system, you can ensure the appropriate size of the inverter for a reliable and efficient power supply, preventing potential damage and ensuring peace of mind.
When matching the inverter size, it is important to take into account the power requirements of the appliances you intend to run. This can be determined by checking the power consumption information provided on the appliance labels or stickers. It is recommended to choose an inverter with 30% extra capacity above the rating of the appliance to account for peak power draw.
Additionally, the maximum discharge specifications of the battery system should be considered to avoid overloading and damaging the batteries. Properly sizing the inverter and ensuring suitable cabling and fuses will help prevent overheating and fire hazards, ensuring a safe and efficient power supply for your appliances.
also read : Maximizing Car Battery Power For Inverter Usage: Key Factors To Consider
Battery System Limitations
Considering the limitations of a battery system is crucial when determining the appropriate size of an inverter. The maximum discharge specifications of the battery system should be taken into account to ensure that the inverter does not exceed the battery’s capacity. Lead acid batteries, in particular, are not designed for heavy loads and using an inverter that exceeds their capabilities can damage the battery and shorten its lifespan. Additionally, the cabling and fuses used in the setup should be suitable for the power requirements to prevent overheating and fire hazards. To help users understand the limitations of their battery system, the following table provides a comparison of different battery types and their maximum discharge current:
| Battery Type | Maximum Discharge Current |
|---|---|
| Lead Acid | 0.2C |
| Lithium Ion | 1C |
| Nickel Cadmium | 1C |
| Nickel Metal Hydride | 0.2C |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate | 0.5C |
By considering these limitations, users can select an inverter size that is appropriate for their battery system and avoid potential damage or hazards.
Safety Measures
To ensure the protection of your battery system and prevent potential hazards, implementing necessary safety measures is crucial when using an inverter. Safety should be a top priority to avoid damaging the batteries or causing fire risks.
It is important to choose an inverter that is suitable for the specific battery system and the appliances being powered. Consideration should be given to the maximum discharge specifications of the battery system and the power consumption of the appliances.
In addition to selecting the appropriate inverter, it is essential to use suitable cabling and fuses to prevent overheating and fire hazards. Following the guidelines provided by the manufacturer and ensuring proper installation and maintenance of the inverter will greatly contribute to a safe and efficient operation.
Always prioritize safety to ensure the longevity of your battery system and the well-being of all individuals involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use an inverter to power my 240V appliances from a 12V battery system?
Yes, it is possible to use an inverter to power 240V appliances from a 12V battery system. However, it is crucial to choose the right size inverter based on the power consumption of the appliances and to consider the limitations of the battery system.
How do I determine the power consumption of my appliances?
Determining the power consumption of appliances is crucial when choosing the right inverter. This can be done by referring to the stickers or labels on the appliances, which indicate their power consumption in watts.
Is it necessary to add a margin for peak power draw when sizing an inverter?
It is necessary to add a margin for peak power draw when sizing an inverter. This ensures that the inverter can handle sudden spikes in power demand from appliances, preventing damage to the inverter and providing a safety buffer.
Can using a larger inverter than recommended damage my battery system?
Using a larger inverter than recommended can potentially damage your battery system. Oversizing the inverter can cause excessive discharge rates, leading to reduced battery lifespan and potential overheating and fire hazards. It is crucial to choose an inverter that suits your appliances and battery system specifications.
What other factors should I consider besides inverter size when setting up my system to prevent overheating and fire hazards?
In addition to inverter size, other important factors to consider when setting up a system to prevent overheating and fire hazards include choosing suitable cabling and fuses, ensuring the battery system’s maximum discharge specifications are considered, and using proper installation techniques.






